At the heart of payment integration is security. Beyond facilitating transactions between parties, security is an exchange of trust. Businesses that store consumers’ credit or debit card information, digital wallets, mobile money, and other sensitive payment details are expected to handle this data responsibly and securely.
This trust is especially critical in the face of Nigeria’s growing e-commerce and other online businesses. A significant number of Nigerians have pivoted to buying on the internet, attracted by the ease, convenience, and access it offers. However, this shift has been accompanied by a concerning rise in fraud and other online vices. These security threats not only jeopardize the financial well-being of businesses but also weaken the foundation of trust on which Internet commerce is built.
In this article, you’ll learn about payment security, types of payment security, and best practices to consider when integrating payment into your application.
What is Payment Security?
Payment security is a set of measures individuals or businesses take to protect financial transactions from fraud and other unauthorized access. These measures range from approval processes organizations implement before authorizing transactions to personal practices, such as safeguarding payment details (e.g., card PINs) from malicious actors. For both online and offline businesses in Nigeria, payment security is important because it helps:
- Minimize financial losses
- Comply with regulatory requirements
- Protect financial data
- Prevent fraud
- Build trust with customers
8 Common Types of Payment Security
When you want to protect and secure your businesses online, there are several types of payment security measures and technologies that you can leverage to protect financial transactions and customer data. Let’s look into some of the common ones:
- Encryption
- Tokenization
- Authentication
- Secure Payment Gateway
- PCI DSS-compliance
- Fraud Prevention
- Security Patches
- Firewall and Network Security
1. Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting sensitive data (like credit or debit card numbers, security answers, and other sensitive payment information) into a coded format to prevent unauthorized access, tampering, and theft. It involves using algorithms and keys to safeguard payment information, ensuring that only individuals with the correct key can access it. The two main types of encryption are:
- Symmetric: Involves using the same key to lock and unlock the data.
- Asymmetric: Involves the use of two keys for safeguarding data: a public key for locking and a private key for unlocking the data.
A popular example of an encryption protocol is Transport Layer Security(TLS), which is used for secure communication over the Internet.
2. Tokenization
Tokenization protects sensitive payment information by replacing it with unique tokens that are irrelevant when compromised. These tokens are reference points to the original data, such as credit card details, which are stored in a centralized token vault. Even if intercepted during the payment processing process, fraudulent actors cannot access the original payment details from the tokens alone.
3. Authentication
Authentication is a security measure that verifies the identity of the user attempting to access or complete a transaction. This additional layer of security for transactions prevents fraud or unauthorized transactions. Common authentication methods include:
- Single-Factor Authentication(SFA): Requires users to log in with a username and a password or pin.
- Two-Factor Authentication(2FA): Requires users to provide two forms of identification, such as a password and a one-time code sent to a registered device.
- Multi-Factor Authentication(MFA): Requires three or more forms of identification, such as physical tokens, biometric data, security questions, and so on.
Authentication methods like 2FA and MFA can improve your business payment security by adding an extra layer of protection to the system.
4. Secure Payment Gateway
A secure payment gateway provides a secure and trusted channel for customers, businesses, and payment processors to transmit payment information. These gateways adhere to payment industry rules and regulations while handling authentication, encryption, and tokenization of cardholder data.
5. PCI DSS-compliance
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards that ensures companies or bodies that process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure and consistent environment. PCI DSS compliance helps businesses:
- Secure networks and systems
- Protect cardholder data
- Manage vulnerability
- Create strong access control measures
- Perform regular monitoring and testing of networks
- Maintain an information security policy
6. Fraud Prevention
Businesses can use techniques like machine learning algorithms, risk scoring, and behavior analysis to monitor transaction patterns, customer behaviors, and other risk factors. These techniques help businesses build payment systems to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions.
7. Security Patches
Regular security updates and patches provided by software vendors and operating system providers help fix payment vulnerabilities, bugs, and other security issues in their products. When businesses take advantage of these fixes, they increase performance, maintain compliance with industry standards, and protect against threats.
8. Firewall and Network Security
Firewalls act as security guards that control the information coming into and going out of a system based on specific rules. They protect payment infrastructures through several methods:
- Network Segmentation: Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the potential damage in case of a security breach, instead of affecting the entire system.
- Traffic Monitoring: Continuously observing network traffic for suspicious activities.
- Access Control Implementation: Utilizing measures like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to ensure that only authorized users can access the network.
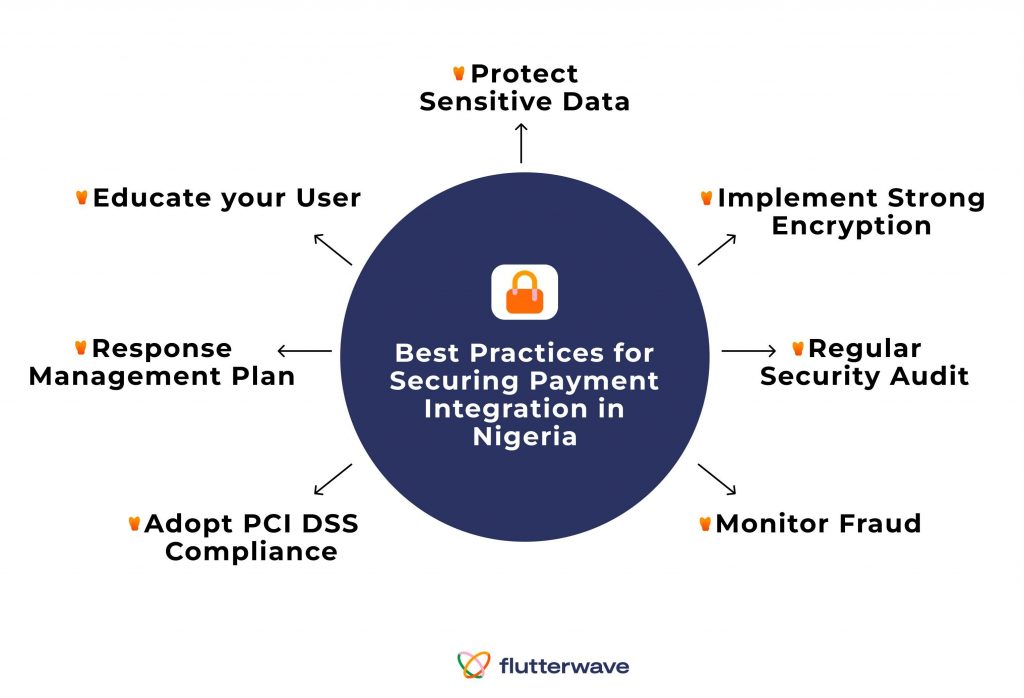
Best Practices for Securing Payment Integration in Nigeria
Security must be at the forefront of your consideration when integrating payment into your application. You want a system that protects your customer’s sensitive data and prevents fraudulent activities. Below are some points you should consider:
- Protect Sensitive Data
- Implement Strong Encryption
- Regular Security Audit
- Monitor Fraud
- Adopt PCI DSS Compliance
- Response Management Plan
- Educate your User
Protect Sensitive Data
Use advanced techniques like tokenization and dynamic data masking to replace sensitive card details when storing or transmitting payment details. This will help you reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Implement Strong Encryption
When customers interact with your application, they’ll transmit payment information. You should use TLS to encrypt data transmitted from your application to a payment gateway. Additionally, they might want to store their sensitive payment information; ensure that you encrypt such data before storing it to prevent unauthorized access.
Regular Security Audit
Security in payment gateways is not a one-time event; it’s a continuous process that must be factored into your workflow. You need to conduct regular vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security weaknesses.
Monitor Fraud
Adopt techniques like machine learning algorithms and behavior analysis to monitor and identify transaction patterns, customer behaviors, and other risk factors.
Adopt PCI DSS Compliance
You need to understand guidelines and principles for storing, processing, and transmitting credit card information. PCI DSS compliance is not just a best practice—it’s a requirement for any business that handles card payments.
Response Management Plan
While preventing security breaches is paramount, it’s crucial to prepare for the possibility that they may occur. Developing a comprehensive incident response plan is essential. This plan should include:
- Clearly defined roles and responsibilities for team members
- Effective communication strategies
- Specific response procedures for various types of breaches or incidents
Having such a plan helps your team respond swiftly, recover quickly, and minimize damage in the event of a security incident.
Educate your Users
Beyond building a robust and secure application, you also need to educate your users about phishing scams, fraudulent activities, and other scheming tactics and the importance of protecting their personal information. Additionally, encourage your users to use unique passwords for their accounts and enable 2FA/MFA as an extra layer of security.
While these best practices ensure your application is robust, secure, and compliant, implementing payment security is resource-intensive and often diverts focus from your core business operations. This is why partnering with a specialized provider can be beneficial. Such a partner can abstract the security complexities, allowing you to concentrate on your users and business growth. Let’s examine in detail how the right partner can assist you.
Manage Payment Integration Security with Flutterwave
Flutterwave is a partner that can reduce your security overheads and other complexities. We handle your payment integration needs with maximum security by providing the following:
- Fraud Protection: When you integrate with Flutterwave for businesses, you don’t have to worry about suspicious activities on your transactions. Our platform provides built-in fraud analysis for your orders and clear indicators to help you decide whether to fulfill or cancel each transaction.
- Account Security: Using Flutterwave to accept payments and payouts requires you to activate two-factor authentication on your account. Anytime you log in, you’ll need to enter your password and a one-time password (OTP) code sent to your email.
- 3D Secure(3DS): With Flutterwave, you can access 3DS checkout flow, an industry standard that makes it easy to process online card payments. It provides an extra layer of security by automatically adding an authentication step during card transactions.
- IP Whitelist: This functionality gives you control over who can access your Flutterwave account to process payouts via the API. If, for any reason, an IP address that’s not whitelisted attempts to transfer from your account, it won’t be successful.
- Certification and Standardization: Flutterwave maintains standards that are higher than required for global operations. We renew our security license and certification annually (e.g., PCI-DSS) to ensure your transactions are safe and secure.
- Periodic Audit: At Flutterwave, security is a continuous process. We work with global security and auditing firms to ensure our payment infrastructure is standardized to protect you and your customers.
- Dedicated Customer Support: As part of the Flutterwave family, you have a dedicated support team for both security-related and general payment integration issues. You can also join our Slack community to stay up-to-date with our latest developments and connect with a vibrant network of users and developers.
Security is an integral part of your payment integration, but you don’t have to break the bank to get it sorted out. Flutterwave has you covered and ensures that both your business and customers are safe and secure.
